In
order to see the 3-D structures presented in this section, you have to
instal the CHIME plugin.
During this tutorial we tried
to elucidate the mechanism by which Substance X arrests the cell cycle.
In
order to see the 3-D structures presented in this section, you have to
instal the CHIME plugin.

During this tutorial we tried
to elucidate the mechanism by which Substance X arrests the cell cycle.
To examine the interactive
structural models click here.
(This will open a new window.)
Follow this tutorial from
beginning to end.
To learn more about the 3-D
structure of CDK2 click
here.
Old version
Go to the "Structural Waters" menu in the top window on the right and
click on the HOH OFF option.
Go to the menu "Basic Structure Presentation" in the top window on
the right and click on COLOR BY CHAIN option. The chains appear
in a wireframe form and the ligand (ATP) appears in a spacefill form.
Using the left button of the mouse rotate the molecule so you can see
the ligand more clearly.
Press SHIFT in your left hand and drag the mouse while pressing
the left button using your right hand - this will enlarge the 3-D structure.
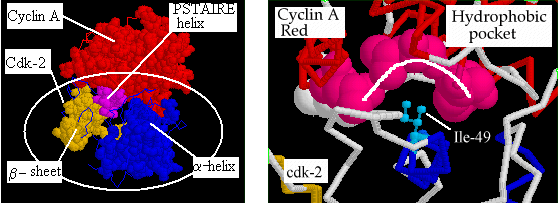
First, we will highlight those residues in CDK2 which are involved
in cyclin binding.
Go to the bottom window. Follow the sequence of chain A and
click on the buttons below the following residues:
R36 ; D38 ; E40 ; E42 ; P45 ; S46
; T47 ; A48 ; I49 ; R50 ; E51 .
Click on COLOR BY CHAIN and rotate the molecule if necessary.
Now we will highlight those residues in cyclin A which are involved
in CDK2 binding.
Go to the bottom window. Follow the sequence of chain B and
click on the buttons below the following residues:
L263 ; K266 ; F267 ; E295 ; L299
; L306 ;
Click on COLOR BY CHAIN and rotate the molecule if necessary.
To examine an interactive structural model of the 3-D structure of CDK2
click here.
(This will open a new window.)