
Question 1
Adapted from: Berg JM, Tymoczko JL & Stryer L, Biochemistry (5th Edition), Chapter 6
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=stryer.section.5115#5128

Some people are found to have difficulty eliminating certain types of drugs from their bloodstreams. The problem has been linked to a gene X, which encodes an enzyme Y.
 Why
does person B exhibit no symptoms?
Why
does person B exhibit no symptoms?
 Analyse
the problem of person C.
Analyse
the problem of person C.
 Analyse
the problem of person D.
Analyse
the problem of person D.
Think,
then check the answer.
 Analyse
the problem of person E.
Analyse
the problem of person E.
Think,
then check the answer.
 Analyse
the problem of person F.
Analyse
the problem of person F.
Think,
then check the answer.
.
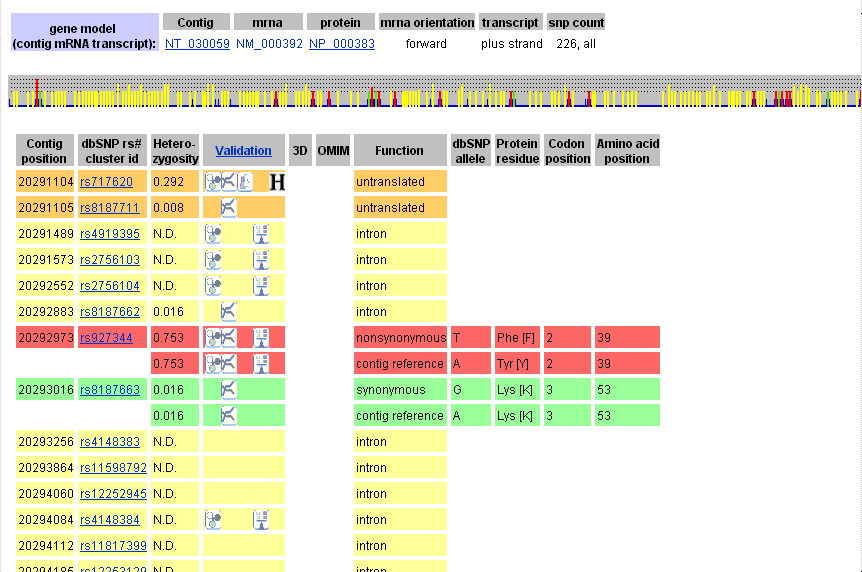
.