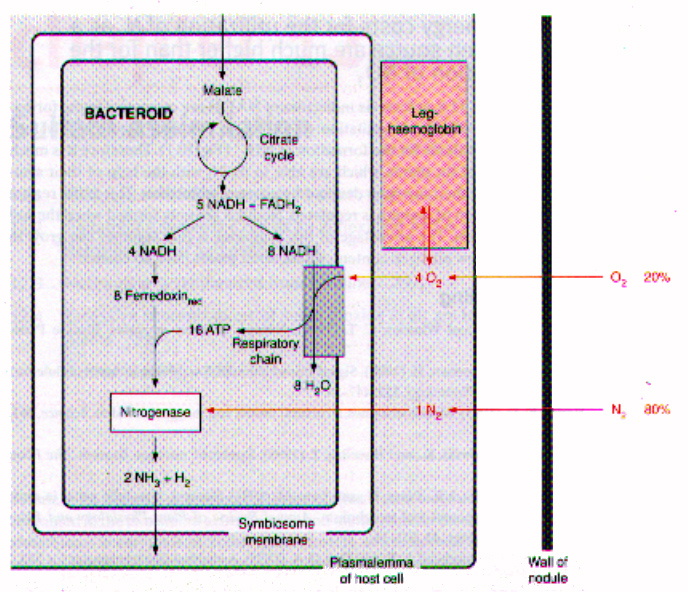

N2 fixation by bacteroids. the total oxidation of malate by the citrate
cycle yields five NDAH and one FADH2. The formation of two NH3 from N2
and accompanying reduction of 2H+ to H2 requires 16 molecules of ATP. Generation
of this ATP by the respiratory chain localized in the bacteroid membrane
requires the oxidation of about eight molecules of NADH. Thus for each
molecule of N2 fixed four molecules of O2 are consumed by the oxidation
of NADH in the respiratory chain of the bacteroid membrane.
![]() To
the Rhizobium-legume association
To
the Rhizobium-legume association