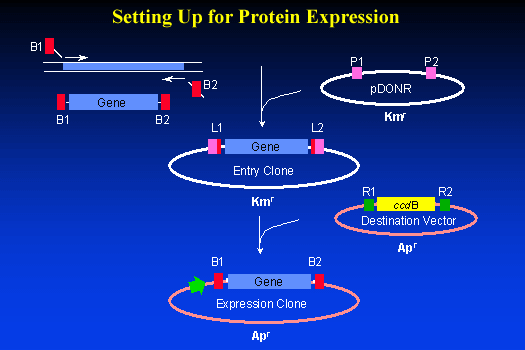
The BP Recombination Reaction
The BP reaction is the first recombination reaction desigend
to insert our gene of interest (in this case the PCR picked ras) into an
Entry Clone. This Entry Clone will be used later for shuttling the gene
into the Expression Clones.
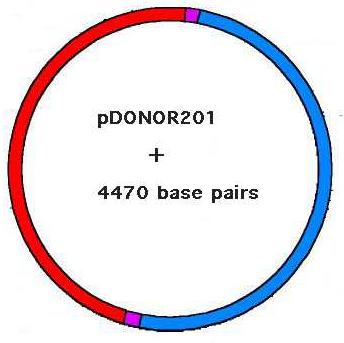
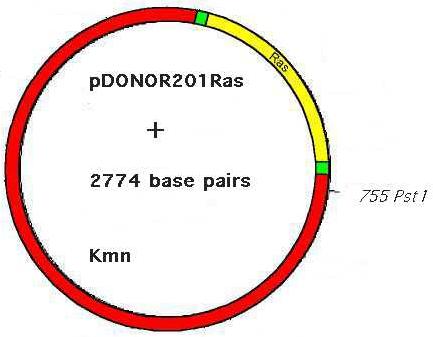
Below you can see the original pDONOR201 and the resulting
pDONOR201Ras that emerges following recombination. During recombination
the
blue fragment
of pDONOR201 containing the toxic ccdB
gene is replaced by the ras
encoding fragment, and the L recombination
sites are formed. Observe the changes
in the plasmid's size following recombination (4750 bp to 2274 bp).
B1RASB1
+ 
You have performed the BP reaction and transformed the
DNA mixture to DH5a cells. In addition, you
transformed other DH5a cells with a mixture of pDONOR201 + a linearized
vector containing a control gene flanked by the appropriate recombination
sites. (This vector is supplied by the manufacturer.)
This system serves as a positive control. You also transformed additional
DH5a cells with pDONOR201 alone. These cells serve as a negative
control.
Here are your results:
|
|
Ras Reaction
|
Positive Control
|
Negative Control
|
|
+ Kan
|
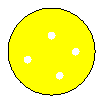
|
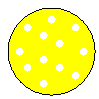
|
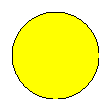
|
|
+ Amp
|

|

|

|

Suggest possible interpratations. (Choose between
possible and wrong.)
Check ALL answers.
-
The colonies of the ras reaction
on the ampicillin plates resulted from a low efficiency BP reaction.
-
Few colonies on Kan plates resulted
from insufficient incubation time of the BP reaction.
-
The PCR product used for the
BP reaction was contaminated with low levels of the non-specific products
(bands 2 and 4).
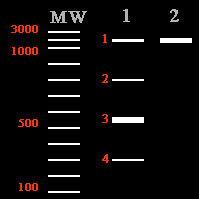
-
The PEG precipitation procedure
didn't proceed properly, and consequently caused the formation of primer-dimers.
-
attB-PCR primers have a mistake
in the attB1 or attB2 sequences.
Continue


